Scabies: Everything you are itching to know
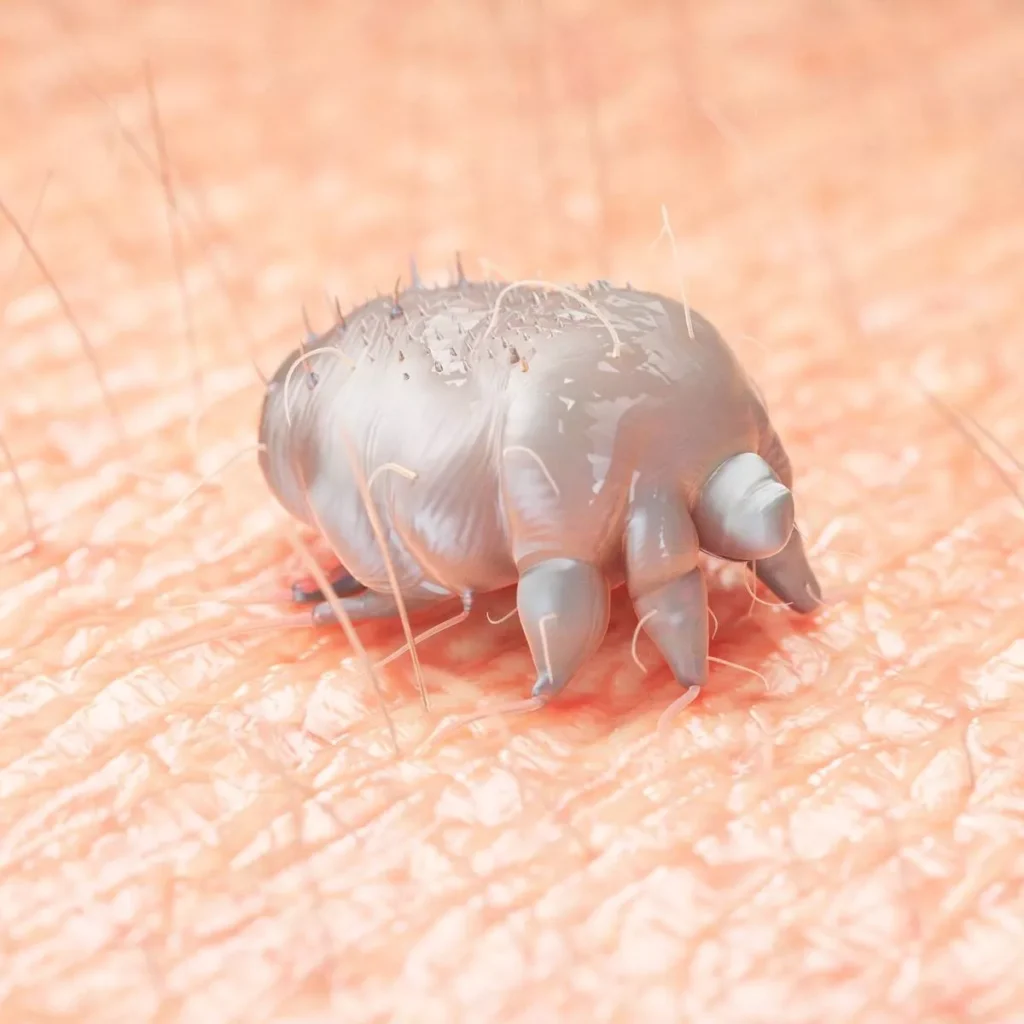
1. Causes and Transmission:
• Scabies is a contagious skin disease caused by the infestation of the skin by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite.
• Transmission occurs through prolonged skin-to-skin contact or, less commonly, through contact with contaminated bedding, clothing, or furniture.
• Crusted (Norwegian) scabies is a severe form that is highly contagious due to the large number of mites present.
2. Symptoms:
• Intense itching, particularly at night.
• Red, raised bumps or burrows, commonly found in the webbing of the fingers, wrists, elbows, and other folds of the skin.
• Crusted scabies involves thick crusts of skin containing mites, making it more infectious.
3. Risk Groups:
• Elderly individuals, immunocompromised patients, and those in crowded or institutional settings (e.g., hospitals, care facilities).
• Healthcare workers are at risk of exposure, especially during outbreaks.
4. Diagnosis:
• Clinical examination of characteristic burrows and rashes.
• Confirmation through skin scrapings viewed under a microscope to detect mites or eggs.
Best Practices for Cleaning Hospital Rooms After Scabies Patients
1. Isolation:
• Patients with confirmed scabies should be isolated until 24 hours after appropriate treatment begins.
• Use dedicated personal protective equipment (PPE) for healthcare workers.
2. Cleaning Procedures:
• Perform terminal cleaning after patient discharge, focusing on thorough disinfection of surfaces and objects that may harbor mites.
• Use disinfectants approved by the hospital for environmental cleaning (e.g., quaternary ammonium compounds or hydrogen peroxide-based solutions).
3. Bedding and Laundry:
• Wash all linens, blankets, and towels used by the patient in hot water (≥60°C) and dry on high heat.
• Items that cannot be washed should be sealed in plastic bags for at least 72 hours to ensure mite death.
4. Furniture and Upholstery:
• Vacuum upholstered furniture and mattresses thoroughly.
• Use steam cleaning where applicable.
• If contamination is suspected, isolate and treat furniture as necessary.
5. Equipment Decontamination:
• Clean and disinfect medical equipment and shared devices using hospital-approved agents.
• Avoid using porous or non-disinfectable materials in high-risk areas.
6. Waste Management:
• Dispose of waste (e.g., used gloves, dressings) in sealed biohazard bags.
• Ensure proper disposal protocols to prevent accidental contamination.
7. Staff and Visitor Protocols:
• Ensure all staff involved in patient care receive prophylactic treatment, if necessary.
• Restrict unnecessary visitation to prevent external transmission.
8. Monitoring and Reporting:
• Monitor for new cases among patients and staff for at least 6 weeks post-exposure.
• Report outbreaks to public health authorities if required.
9. Education and Awareness:
• Provide training for healthcare workers on recognizing and managing scabies.
• Emphasize proper hand hygiene and the use of PPE to minimize transmission risks.
Key Challenges
• Crusted Scabies Management: Requires intensive environmental cleaning and potentially mass treatment of contacts.
• Outbreak Control: Institutions like hospitals and nursing homes may face challenges due to the fast transmission rate and asymptomatic carriers.
Cleaning Agents for Environmental Control
Disinfectants
• Quaternary Ammonium Compounds (QACs):
• Effective against mites on hard surfaces.
• Commonly used for cleaning floors, walls, and furniture.
• Hydrogen Peroxide-Based Solutions:
• Broad-spectrum efficacy, including against microbes and mites.
• Ideal for high-touch areas like doorknobs, bed rails, and medical equipment.
• Steam Cleaning:
• Excellent for upholstered furniture, carpets, and mattresses where chemical cleaning is insufficient.
• Mites are killed at temperatures >60°C.
Vacuuming
• Use vacuums with HEPA filters to capture fine particles, including mites and eggs.
• Focus on areas like bed crevices, chairs, and carpets.
Sealing Contaminated Items
• Items that cannot be cleaned (e.g., books, non-washable fabric) should be sealed in plastic bags for 72 hours or longer.
Laundry
• Wash all textiles in hot water (≥60°C) and dry on high heat for at least 30 minutes.
• For items that cannot be washed, use a dryer at the highest heat setting.